What makes Nopal so good?
Many scientists now believe that nature holds the key to good health and that because we have strayed away from the natural diets of our ancestors, we have lost much of the photochemical protection from disease that is offered in nature, by plants in particular. Additionally, the modern diet typically contains large amounts of saturated animal fats, hydrogenated oils, calories, sodium and other ingredients that, when added to the environmental contaminates characteristic of industrial societies, renders the human body more susceptible to disease.
Today there is great interest in finding and developing products from nature that possess the power to sustain, heal and manage the human body system in a way that promotes better living and freedom from conditions that can debilitate the human body and spirit. VHP is one of those companies.
Nopal...
- Simultaneously affects several major body systems in a synergistic way
- Is rich in nutrients that strengthen the liver and the pancreas and improve body cell response to insulin stimulation.
- Helps the body pull fluid from body tissues back into the bloodstream
- Reduces the risk of heart disease
Before introducing NopalActiv® to the market, we engaged in a quest to re-discover the lost secrets of natural products - natural products that strengthen the systems of the human body and their ability to internally resist disease and the effects of aging. That quest involved a wide variety of natural plants and herbs. But, we found only one plant that has
benefits for the total human body system. For centuries, and even today in out-of-the-way-places lacking the availability of nearby or accessible modern medical resources, it is used as a basic food source and medicinal. Its common name in its native country of Mexico is Nopal. It is sometimes referred to as prickly pear cactus. Nopal is classified by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) as a vegetable. Its scientific name is Opuntia Ficus-indica.
Glandular System
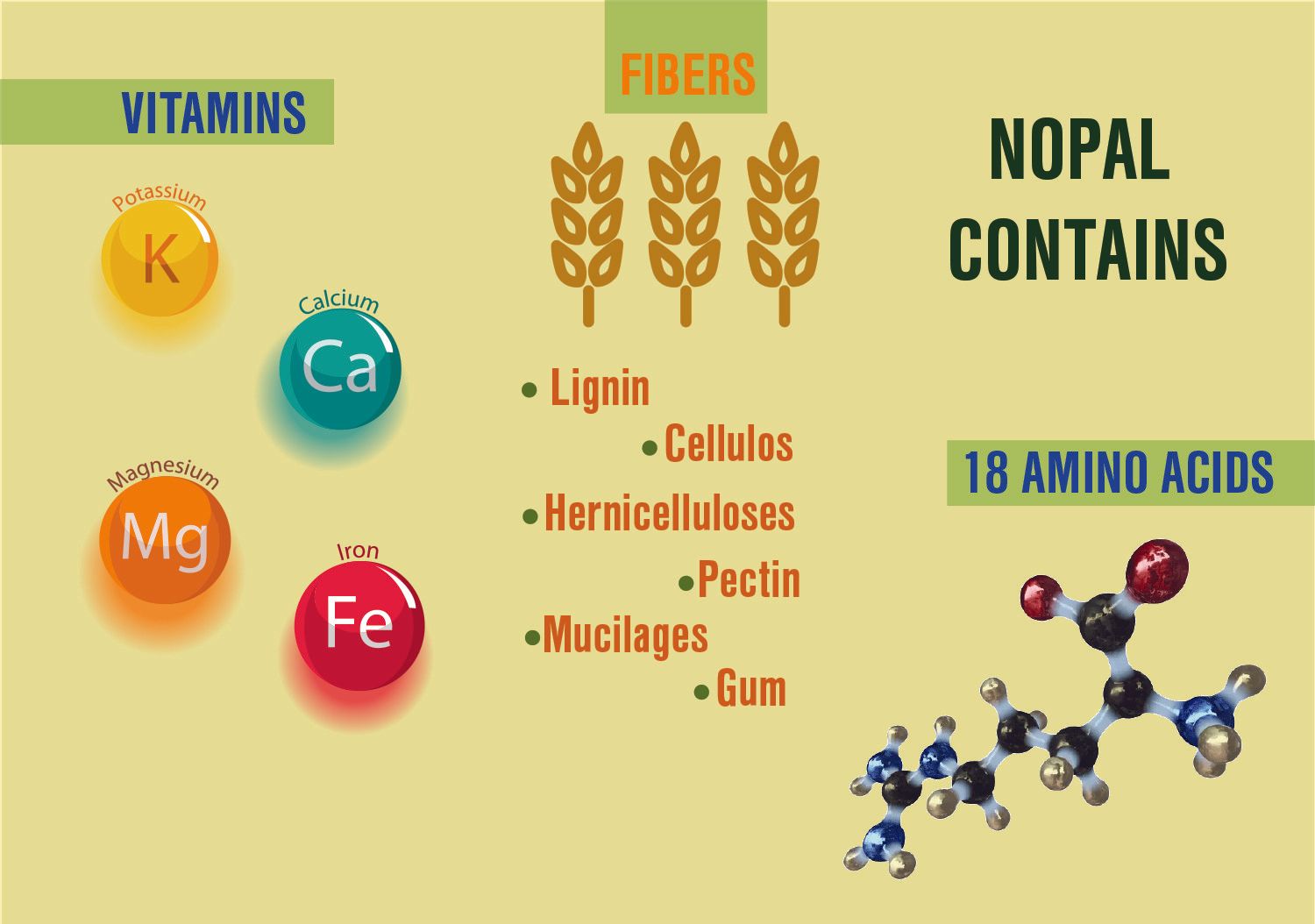
In comparison with other plants, Nopal is rich in nutrients that strengthen the liver and the pancreas. The health of these two organs is vitally important to the production of insulin and the conversion of carbohydrate sugars into glycogen (stored in the liver and body cells) useable as energy by the body. Vitamins found in Nopal (A, B1, B2, B3, and C), minerals (Calcium, Magnesium, Potassium and Iron) and Fibers (Lignin, Cellulose, Hernicelluloses, Pectin, Mucilages, and Gum), along with the 18 amino acids also found in Nopal help to strengthen, detoxify and support the function of the liver and pancreas.
Additionally the ingredients in Nopal improve body cell response to insulin stimulation, which is necessary to move glucose from the blood stream into body cells where it is used as energy.
The active ingredients found in Nopal aid in preventing the digestive system from absorbing excess dietary fat and carbohydrate sugars, thereby helping to maintain proper blood sugar balance and control obesity.
Soluble fibers in Nopal (including gums, mucilages, pectins, polysaccharides and some hemicellulose) slow the absorption of glucose in the intestines. The pectin found in Nopal is also known for increasing satiety (decreasing appetite). These are important factors in controlling obesity.
Insoluble fibers (more commonly known as roughage); reduce excess bile and potential carcinogens (cancer causing agents) that may be present in the colon, by absorption and excretion. Insoluble fibers of the Nopal plant include cellulose, lignin and remaining hemicellulose.
Nopal is a gentle alternative to psyllium (a well-known fiber supplement taken for colon cleansing) for those with a sensitivity or allergy to psyllium.
The vegetable protein found in Nopal (amino acids) help the body pull fluid from body tissues back into the bloodstream thereby diminishing cellulite and fluid retention. Fat build up is prevented while fat break down and excretion is increased.
Research has found that the natural photochemical ingredients in Nopal act synergistically and simultaneously in positively impacting several human body systems. For example, Hospital-based clinical studies have consistently found that Nopal has a clear hypoglycemic effect on obese, insulin-resistant Type 2 Diabetic patients; while simultaneously lowering serum levels of low-density cholesterols and triglycerides. Nopal is rich in pectin (a soluble fiber), but in addition to fiber-related inhibition of glucose absorption, fasting glucose is also significantly lowered, indicating that Nopal also has the highly beneficial effect of increasing the body's sensitivity of insulin.
Animal studies corroborate this finding, showing that small amounts of an active fraction isolated from Nopal can partially reverse Diabetes. Similar effects on reduced serum levels of low-density cholesterols (LDLs) and triglycerides not entirely explained by fiber absorption were found, indicating that Nopal has a simultaneous and highly beneficial effect on hepatic function. Consequently, it appears that Nopal simultaneously affects several major body systems in a synergistic way.
Among the body systems that have been reported to be most affected by the dietary ingredients and other phytochemicals found in Nopal are the glandular, digestive, immune, circulatory, urinary and nervous systems.
Diabetes, heart conditions and cancer have been scientifically related to deficiencies in these systems.
Circulatory System
Nopal acts in several ways that have been found to reduce the risk of heart disease. First, the fiber found in Nopal acts to absorb and excrete cholesterol in the digestive system. Second, the amino acids, fiber and B3 (niacin) found in Nopal prevent excess sugar conversions into fats, while reducing triglycerides and LDL cholesterol levels, by metabolizing fat and fatty acids and eliminating excess bile acids that would eventually convert into cholesterol. Third, the B3 (niacin) in Nopal acts to convert LDL (bad) cholesterol to HDL (good) cholesterol. Additionally, the amino acids and fiber, together with the anti-oxidant effect of the vitamin C, Carotene (precursor to Retinol vitamin A) and selenium found in Nopal aid in preventing blood vessel wall damage (hardening of the arteries) and the formation of fatty plaques in the arteries (arteriosclerosis and atherosclerosis).
Nervous System
Amino Acids found in Nopal (including Alanine, Aspartic Acid, Phenylalanine and Serine play a role in maintaining healthy nervous system cells and aid in the balancing the nervous system, which creates a sense of well being. Nopal helps prevent Diabetic Neuropathy.
Immune System
Phytochemicals are powerful allies of the body's immune system allowing it to defend the body against pathogens. One group act as "anti-oxidants" in eradicating oxygen deficient molecules known as "free radicals" that if not eliminated, cause cell damage that can lead to diabetes, cancer, heart disease and other disorders. A second group act as "detoxifiers" by supporting normal processes that allow the human body to recognize and destroy or eliminate toxic substances ingested or produced by other reactions within the human body. A third group act as "hormone modulators" by triggering needed hormone production (such as insulin) and by substituting harmless substances (such as phytoestrogen) for over-acting natural hormones that can trigger cellular damage and lead to cancer. A fourth group act as "cell regulators" by assisting the human body control the rampant growth characteristics of tumors. Recent studies have found that among the phytochemicals found in Nopal are the types that inhibit cancerous cell growth and may even help prevent cancer from developing. Animal studies corroborate this showing that dosages of Nopal juice increase immune system efficiency in controlling tumor growth, Epstein-Barr virus and suppressed immune response.